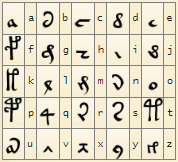
Voynich EVA Cipher
The Voynich EVA cipher refers to a specific method of transcribing the Voynich manuscript's text into a more manageable format for analysis. EVA stands for "Extensible Variant Alphabet," a system developed by researchers to provide a consistent and systematic way to represent the manuscript's unique script.
Key Aspects of the Voynich EVA Cipher:
Transcription System:
The EVA system maps the complex characters of the Voynich script into a standardized set of Latin characters and symbols. This transcription helps researchers to analyze the text more easily, even though the original meaning remains undeciphered.
Purpose:
The EVA transcription aims to create a uniform representation of the manuscript's script to facilitate comparative analysis, statistical study, and cryptographic attempts. By using EVA, researchers can work with a consistent representation of the text, which is essential for understanding patterns and frequency distributions.
EVA Characters:
The EVA system includes characters that correspond to the unique symbols found in the Voynich manuscript. It categorizes characters into several groups based on their appearance and usage. For example:
- Basic characters: Represent individual symbols.
- Diacritical marks: Used to denote variations or combinations of characters.
Usage in Analysis:
By converting the Voynich script into EVA, researchers can apply various analytical techniques, such as frequency analysis and pattern recognition, which are crucial for cryptographic decryption efforts.
Research Tool:
EVA is one of several transcription systems used by Voynich manuscript researchers. It allows for consistent and systematic examination of the text, helping to identify possible linguistic or cryptographic features.